By Fujie Fan and David Chen, Stream Computing
Background:
In order to solve the problem of instruction fragmentation of RISC-V in AI field and accelerate the pace of AI industry, in 2021, Stream Computing launched open source work on the RISC-V matrix instruction set and supporting tools v0.1, to improve the compatibility of AI applications, reduce the costs of software development, and aim to achieve a new generation of standard and scalable domain specific architectures.
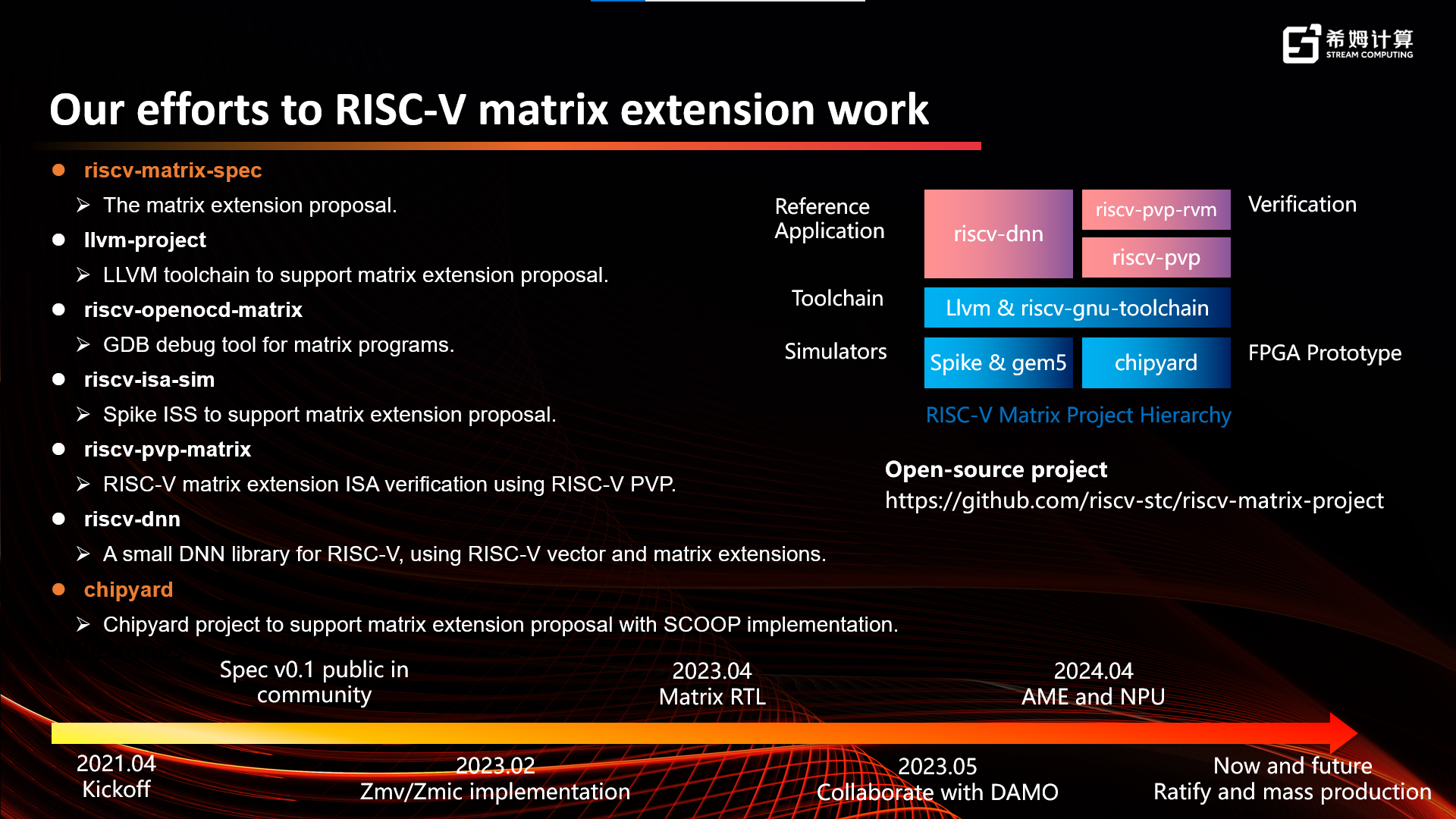
- September 2022, finished the v0.1 of RISC-V Matrix ISA Specification and submitted an open-source proposal and supporting tools to RISC-V International Foundation.
- May 2023, a negotiation mechanism has been established with Damo Academy to jointly explore the RISC-V matrix instruction set.
- August 2024, the v0.5 of RISC-V Matrix ISA Specification was finished.
- October 2024, the supporting toolchains for RISC-V Matrix ISA Specification v0.5 were developed and completed.
Today, Stream Computing officially releases the v0.5 of RISC-V Matrix Instruction Set and its supporting tools, becoming the first company to submit a complete RISC-V matrix instruction set and its supporting tools to the whole global community. It will promote the rapid formation of international standards for the RISC-V matrix instruction set and accelerate the development of the entire RISC-V ecosystem.
Highlights:
- The latest RISC-V Matrix Instruction Set is designed with tile-based matrix multiplication architecture, which further improves the programming model and type support on the original basis.
- A basic version with 32-bit instruction encoding (https://github.com/riscv-stc/riscv-matrix-spec) and an extended version with 64-bit long instruction encoding (https://github.com/riscv-stc/riscv-matrix-spec/tree/matrix64) are both provided.
- Through parameterized register architecture and modular type system, it can adapt to various application scenarios from edge to cloud.
- To promote the standardization and commercial implementation, following tools are provided and updated:
- an LLVM-based compiler (https://github.com/riscv-stc/llvm-project/tree/matrix),
- a Spike-based simulator (https://github.com/riscv-stc/riscv-isa-sim),
- a GDB debugger (https://github.com/riscv-stc/riscv-openocd-matrix/tree/matrix)
- an open-source core implementation based on SCOOP (Stream Computing Out-of-Order Processor) platform that come with RVV and RV Matrix (https://github.com/riscv-stc/chipyard)
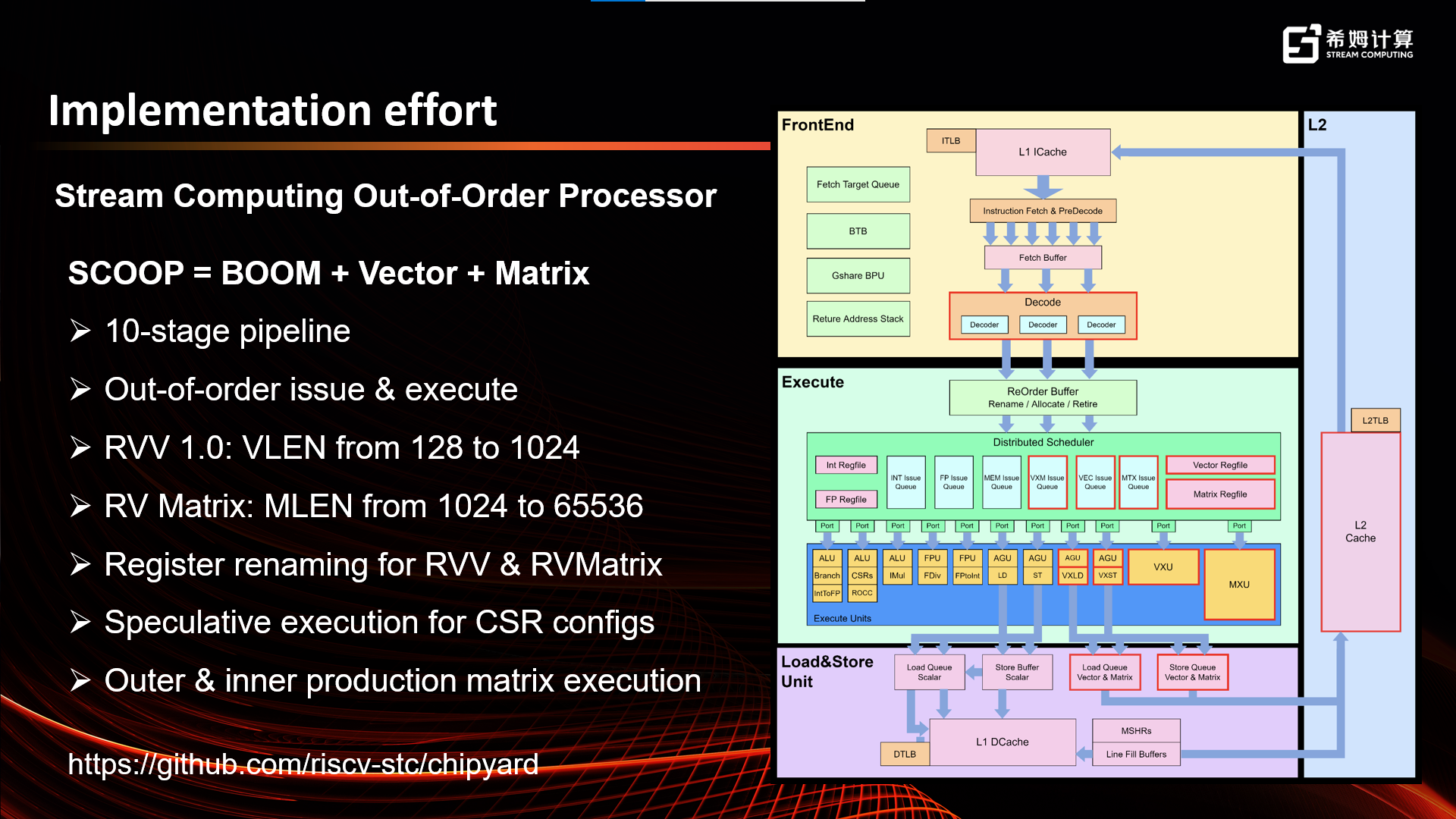
The SCOOP open-source platform adds RVV 1.0 and Matrix supports to the Berkeley BOOM core, making it the first open-source RISC-V Vector and Matrix project in the industry.
At present, the compiler, simulator and debugger have been updated to v0.5. The open-source core has been updated to v0.2, and will gradually be updated to the latest version in the future.
Community Response and Evaluations:
Dr. Fujian Fan, R&D Director of Stream Computing, stated: “We are very excited to launch this new version. By introducing support for the RISC-V Matrix Instruction Set Extension, we believe we can greatly enhance Stream Computing’s capabilities in developing high-performance AI chips based on RISC-V architecture, while contributing to the improvement of RISC-V instruction set. Additionally, our SCOOP implementation with the Chipyard project provides an excellent opportunity to showcase how these advanced technologies can be applied in real-world hardware designs.”
Calista Redmond, CEO of RISC-V International, also gave high praise for the upgrade: “It is truly inspiring to see innovative projects like Stream Computing actively adopting and supporting new features of RISC-V. The Matrix Instruction Set Extension represents a significant step forward for the RISC-V ecosystem, capable of significantly enhancing performance in specific application scenarios. We are grateful for the efforts of the Stream Computing team, which is a tremendous victory for the entire community.”
“We are very excited to collaborate with Stream Computing and introduce RISC-V AI core technology into our classrooms. Through hands-on learning with specific engineering cases, our students will be able to engage with the most cutting-edge technologies and development trends. This will significantly enhance their practical skills and innovation capabilities,” said Dr. Tianyu Jia, Assistant Professor at Peking University, who already chose SCOOP project into his graduate course about SOC design in this fall semester.
Future outlook:
The open-source nature of RISC-V has attracted a lot of attention from academia and industry, and its modular design and scalability capabilities have satisfied the application needs of AI computing power in recent years. AI chips based on RISC-V architecture can not only achieve high computing power required for AI applications, through extended instructions, but also have significant advantages in programming flexibility due to compatibility with the RISC-V standard instruction set.
We look forward to more partners joining this open-source project, driving continuous advancements in computing technology. Stream Computing will continue to work with partners to promote the development of RISC-V in the AI field and prosper the RISC-V ecosystem, to improve the compatibility of AI applications, reduce the costs of software development, and achieve a new generation of standard and scalable domain specific architectures.


